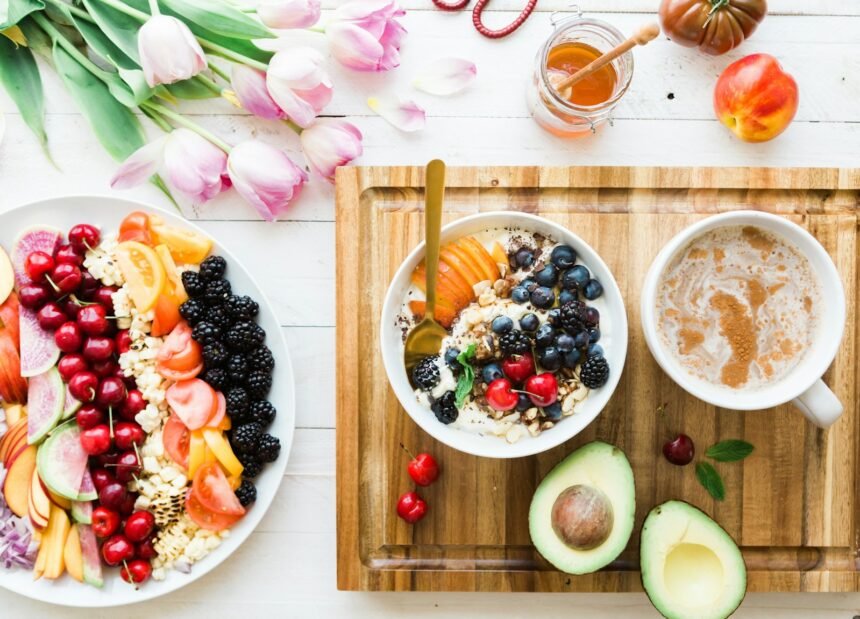
A plant-based diet is gaining popularity as more people look for healthier, sustainable, and ethical ways of eating. A plant-based diet focuses on foods derived from plants. These include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This focus can provide numerous health benefits. This article will explore the health benefits of a plant-based diet. It will also discuss how to transition into it. Additionally, it provides practical tips to make it easier.
What is a Plant-Based Diet?
A plant-based diet focuses on eating whole, unprocessed plant foods. This includes:
- Fruits and vegetables: Fresh, frozen, or dried fruits and vegetables are central to a plant-based diet.
- Whole grains: Foods like oats, quinoa, brown rice, and barley.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and peas are excellent sources of protein.
- Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds offer healthy fats and protein.
- Plant-based alternatives: Tofu, tempeh, and plant-based milk like almond, soy, or oat milk.
Unlike vegan or vegetarian diets, a plant-based diet prioritizes whole and minimally processed foods. It focuses less on excluding animal products.
Health Benefits of a Plant-Based Diet
Eating more plant-based foods can offer significant health benefits, both short-term and long-term. Below are some of the key advantages:
1. Improved Heart Health
A plant-based diet can reduce the risk of heart disease by:
- Lowering cholesterol: High-fiber foods, like oats, fruits, and vegetables, help lower “bad” LDL cholesterol.
- Reducing blood pressure: Plant-based diets are rich in potassium and antioxidants, which help regulate blood pressure.
- Reducing inflammation: Many plant foods have anti-inflammatory properties, which are beneficial for heart health.
Studies show that people who follow a plant-based diet tend to have lower risks of high blood pressure. They also have a decreased risk of heart disease and strokes.
2. Weight Management
A plant-based diet may assist in weight loss or maintaining a healthy weight because:
- Lower calorie intake: Many plant-based foods are naturally lower in calories compared to animal products.
- High fiber content: Foods like beans, vegetables, and whole grains are high in fiber. This keeps you full longer. It reduces the chances of overeating.
Research has shown that individuals on plant-based diets tend to have a lower body mass index (BMI). They may also experience healthier weight loss.
3. Increased Energy Levels
Plant-based foods are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can boost your energy levels, such as:
- Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits and leafy greens, it helps with immune function and energy.
- Iron: Plant-based iron sources like spinach and lentils help prevent fatigue.
- Complex carbohydrates: Whole grains provide steady energy without the energy crashes often associated with processed foods.
People on plant-based diets often report feeling more energetic and less sluggish, which can enhance daily productivity.
4. Better Digestive Health
A plant-based diet promotes a healthy digestive system by:
- Improving gut health: Plant foods are rich in fiber, which helps move food through the digestive system.
- Reducing the risk of constipation: Fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and legumes help keep the digestive tract running smoothly.
- Supporting healthy microbiota: A diet high in plants can help balance the good bacteria in the gut. This leads to better digestion.
Good digestive health is linked to improved immune function, reduced inflammation, and better overall wellness.
5. Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases
Research suggests that a plant-based diet can reduce the risk of developing several chronic conditions, including:
- Type 2 diabetes: Focus on whole plant foods. This approach lowers the risk of type 2 diabetes. It helps achieve better blood sugar control.
- Cancer: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants may reduce the risk of certain types of cancer.
- Chronic inflammation: Plant-based diets reduce chronic inflammation, which is a key factor in many chronic diseases.
Eating more plant-based foods is a powerful step toward preventing long-term health issues.
How to Transition to a Plant-Based Diet
Transitioning to a plant-based diet doesn’t need to be difficult. Here are some steps to make the shift easier:
1. Start Slowly
Rather than completely overhauling your diet overnight, consider making small changes, like:
- Replacing one meal a day with a plant-based choice.
- Substituting dairy milk with plant-based milk (like almond or soy milk).
- Trying plant-based versions of your favorite meals, like veggie burgers or tofu stir-fries.
2. Learn New Recipes
Eating plant-based doesn’t mean giving up delicious meals. There are endless recipes that feature plant-based ingredients. Look for healthy recipes like:
- Smoothie bowls: Packed with fruits, vegetables, and plant-based protein.
- Lentil stew: A hearty meal with plant-based protein and plenty of flavor.
- Chickpea salad: A fresh and filling salad with healthy fats, fiber, and protein.
Experiment with new ingredients and flavors to make the transition enjoyable.
3. Ensure Nutritional Balance
A plant-based diet offers many health benefits. However, it’s essential to ensure that you’re getting all the nutrients your body needs. Some nutrients to keep in mind are:
- Protein: Make sure to include plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, tofu, and quinoa.
- Vitamin B12: This is important for nerve health. Consider B12 supplements or fortified foods.
- Iron: Incorporate iron-rich foods like spinach, lentils, and fortified cereals.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are great plant-based sources.
4. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water is essential, especially when increasing fiber intake. Aim for at least 8 cups of water daily to stay hydrated and support digestion.
Practical Tips for a Plant-Based Lifestyle
To make adopting a plant-based diet easier, here are some helpful tips:
- Meal prep: Plan your meals ahead of time to avoid reaching for less healthy options.
- Shop smart: Keep your pantry stocked with healthy staples like beans, grains, nuts, and frozen vegetables.
- Get support: Find a community or join online groups for plant-based eaters to share tips and recipes.
Conclusion
Switching to a plant-based diet is a fantastic way to boost your overall health. From heart health to improved digestion and energy levels, the benefits are clear. Start small. Learn new recipes. Make sure proper nutrition. Then you can enjoy the many advantages of eating more plant-based foods. Take it one step at a time, and soon you’ll be enjoying a healthier, more sustainable lifestyle.